Direct electrolysis systems turns waste alkaline water into clean hydrogen [View all]
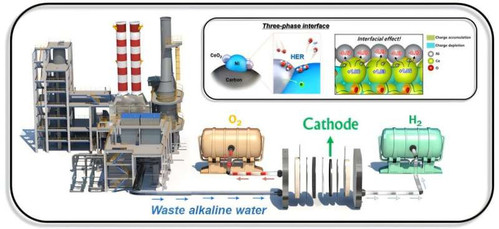 Anion exchange membrane water electrolysis for clean hydrogen production by directly utilizing waste alkaline water generated in industry. Credit: Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS)
Direct electrolysis systems turns waste alkaline water into clean hydrogen
Anion exchange membrane water electrolysis for clean hydrogen production by directly utilizing waste alkaline water generated in industry. Credit: Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS)
Direct electrolysis systems turns waste alkaline water into clean hydrogen
National Research Council of Science & Technology | July 21, 2025
Dr. Sung Mook Choi and his research team at the Energy & Environmental Materials Research Division of the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS) have successfully developed a highly durable non-precious metal-based hydrogen evolution catalyst for use in a direct electrolysis system employing waste alkaline water and anion exchange membranes (AEM). This breakthrough enables the production of clean hydrogen by directly utilizing alkaline wastewater generated from industrial processes.
Notably, the developed catalyst was applied to a commercial-scale 64 cm² single-cell electrolysis system and demonstrated high hydrogen production efficiency with less than 5% performance degradation even after more than 2,000 hours of continuous operation—showing strong promise for real-world application.
Waste alkaline water is generated in large volumes from semiconductor manufacturing and metal etching/cleaning processes. However, due to the high cost of treatment and the potential environmental hazards, its reuse has remained economically inefficient.
Anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) is considered a suitable method for directly utilizing waste alkaline water without the need for separate purification. Nonetheless, impurities and ions contained in the waste water have long interfered with the electrochemical reactions during electrolysis, significantly reducing hydrogen production efficiency...more
https://techxplore.com/news/2025-07-electrolysis-alkaline-hydrogen.html
